Remote Patient Monitoring: Detailed Guide for Healthcare Providers
Keyur Patel
September 12, 2025
12 min
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) applications are revolutionizing healthcare by enabling real-time tracking of patients’ health data outside clinical settings. With advancements in remote patient monitoring software development, healthcare providers can now improve patient care, reduce hospital readmissions, and optimize treatment plans. In this guide, we’ll explore the top remote monitoring applications, key remote patient monitoring use cases, and the critical aspects of remote patient monitoring app development.
What Are Remote Patient Monitoring Applications?
RPM applications leverage wearable devices, mobile apps, and cloud-based platforms to collect and transmit health data, such as:
Heart rate and ECG readings
Blood glucose levels
Blood pressure monitoring
Oxygen saturation (SpO2)
Medication adherence tracking
These apps empower healthcare providers with real-time insights, enabling proactive intervention and personalized care.
Basic Information on Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote patient monitoring is defined as the process of obtaining medical and health information from patients at a distance and then using information technology to transfer that information electronically data interchange to another location for interpretation and feedback. Such a strategy is useful in the assessment of patients’ outcomes and other health parameters beyond the clinical setup.
The healthcare industry is increasingly embracing Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) as a critical technological solution. This trend is driven by demographic shifts, including an aging population and rising chronic disease prevalence, as well as the urgent need for enhanced healthcare efficiency. digital health monitoring offers significant advantages by enabling early detection of potential health issues and allowing timely interventions. This proactive approach leads to improved patient outcomes, reduced hospital readmissions, and more cost-effective healthcare delivery. Complementing RPM, hospital inventory management plays a crucial role in optimizing healthcare operations through systematic tracking and control of medical supplies, equipment, and pharmaceutical resources.
Telemonitoring is especially useful for chronic diseases including diabetes, hypertension heart diseases, and others. It enables healthcare providers to monitor patients’ status in real-time, modify the treatment plans to reflect the changes and respond to the changes in patient’s conditions. Such a strategy can help avoid adverse effects, limit the use of the emergency department, and increase the quality of life in patients.
Key components of an RPM system
To fully appreciate the potential of digital health monitoring, it is crucial to understand the key components that constitute an RPM system
Patient-facing devices and wearables
These include blood pressure monitoring devices, glucose meters, pulse oximeters, and smartwatches that have functions for tracking different parameters. In the realm of fitness app development, these wearables are becoming increasingly sophisticated, capable of measuring multiple health signs simultaneously and offering a comprehensive picture of a patient’s health condition. Current advanced wearables can track various physiological metrics, providing real-time insights that support both medical monitoring and personal health management.
Connectivity solutions
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) systems rely on various connectivity solutions to transmit data from patient devices to healthcare practitioners. These solutions include cellular networks, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi, among others. The choice of connectivity solution depends on several factors, such as the volume of data to be transferred, the frequency of data transfers, and the patient’s location.
Data collection and transmission
The system has to capture and transfer the patient information in real-time or at certain intervals and make sure that the healthcare providers are always up-to-date. This process includes conversion of data into an encrypted form, reducing the data size, and checking for errors in the data.
Healthcare provider interfaces
These are the tools to which doctors and other healthcare personnel log in to see patient records, set alarms, and interact with the patient. These interfaces may consist of graphical displays that provide an overview of multiple patients’ data at once, as a way of managing many patients.
Integration with existing healthcare systems
The RPM solutions should be compatible with Electronic Medical Records (EMR), patient portals, and other healthcare IT structures to deliver full-spectrum patient care. This integration ensures that the patient’s record of health is well captured and the current state of the patient is well understood.
Creating RPM Web and Mobile Applications
The effectiveness of a custom remote patient monitoring system is directly tied to the effectiveness of its web and/or mobile applications. Here are some key considerations when developing RPM apps: Here are some key considerations when developing RPM apps:

Designing user-friendly interfaces
Patients and healthcare providers require natural, appealing, and simple interfaces through which information can be provided in a comprehensible manner and with which the patient can interact easily. For the patients, this could be basic forms to input data, pill boxes, and concise health information. For healthcare providers, it could mean having features such as flexible and adjustable panels with the information of patients who need attention the most and the ability to open a patient’s full file.
Ensuring secure data transmission and storage
Since health information is considered sensitive, it is crucial to implement robust security measures to protect patient data and comply with HIPAA regulations. This includes encrypting data, voice, and messages, utilizing secure authentication methods, and performing regular security audits.
Integrating with various RPM devices and wearables
The application should be able to interface and exchange data with a plethora of monitoring devices to get various health information. This involves the use of several protocols in communication and also the aspect of interoperability with other manufacturers of the devices.
Real-time data visualization and analytics
Similarly, the use of data visualization such as graphs, charts, and other related tools will assist the healthcare mobility solutions providers in easy analysis of the data and enable them to arrive at the right decision within a short time. It also reveals the population’s health status and could be used to forecast possible health risks.
Customization and scalability
Healthcare organizations may require different features in EMR software thus the application should be customizable to different organizations and as the number of users increases.
This might include such aspects as modular building of the architecture, adjustable and expandable alerts and thresholds, and the possibility to extend the system with new features or interfaces to other systems.
Key Remote Patient Monitoring Use Cases
1. Chronic Disease Management:- RPM helps manage chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and COPD by continuously tracking patient vitals and alerting providers to any anomalies.
2. Post-Surgical Recovery Monitoring:- Patients recovering from surgery benefit from remote monitoring apps that track healing progress, pain levels, and mobility metrics.
3. Elderly and Home Healthcare:- Seniors and individuals with mobility challenges can receive continuous care without frequent hospital visits, improving their quality of life.
4. Telemedicine Integration:- RPM seamlessly integrates with telehealth services, allowing physicians to monitor patients remotely and adjust treatments accordingly.
5. COVID-19 & Infectious Disease Monitoring:- Real-time monitoring of symptoms and vitals helps in managing pandemic-related health concerns efficiently.
Challenges in RPM App Development
While the potential benefits of remote health monitoring are significant, developers encounter several challenges when creating RPM applications.
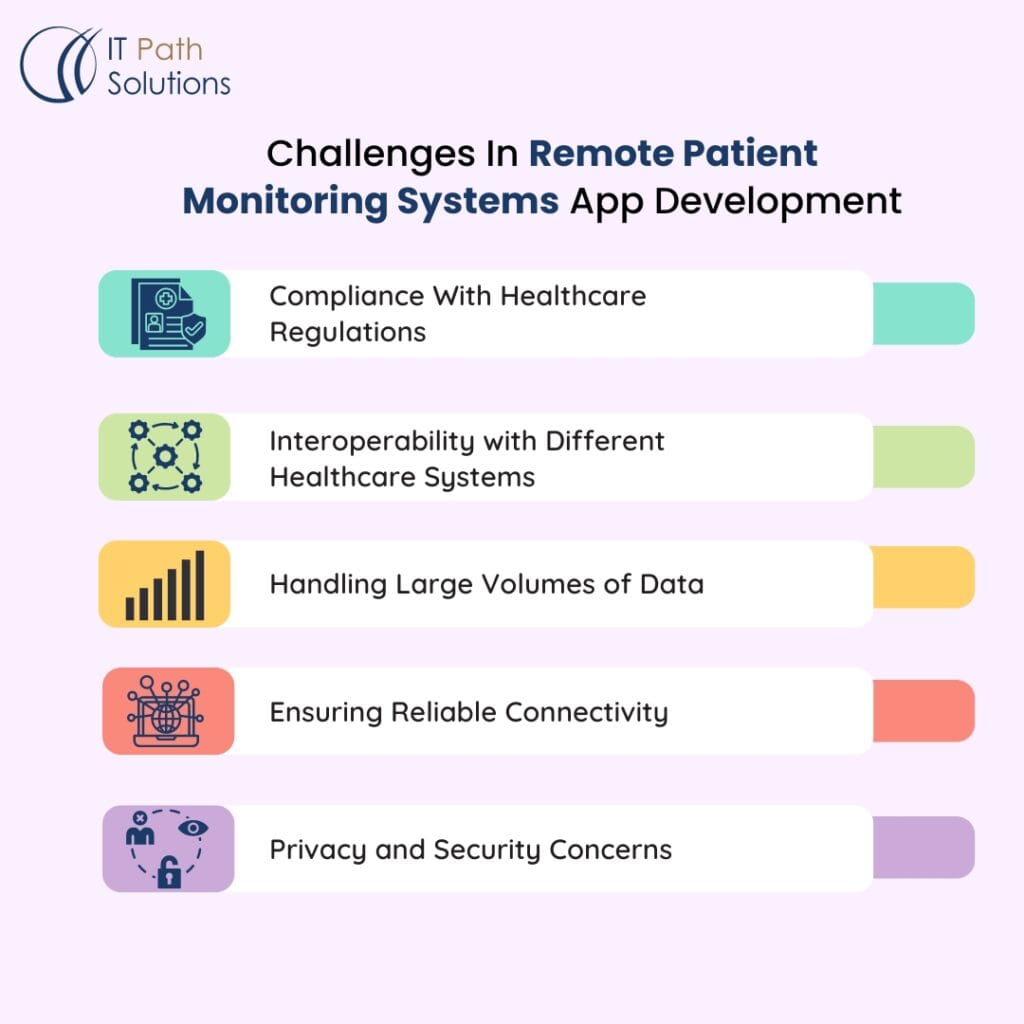
Compliance with healthcare regulations
Compliance with standard protocols like HIPAA and FDA is mandatory to protect the privacy of the patient and his/her data. This means that the application has to have strict measures of data protection and audit trails, as well as all the features in the application conforming to the regulations.
Interoperability with different healthcare systems
The integration of the proposed solution with different varieties of EMR systems and other components of healthcare IT architecture may be challenging due to the dissimilarities in the standards. To integrate with other systems, developers have to use HL7 Integration and FHIR standards for data exchange.
Handling large volumes of data
RPM systems produce huge volumes of data that have to be captured, sorted, analyzed, and archived. This means that there is a need to have strong DBMS, good algorithms for processing data, and good cloud support.
Ensuring reliable connectivity and data transmission
Sustaining data continuity is crucial for patient surveillance, particularly in regions characterized by weak network connectivity. Some requirements need to be fulfilled by developers and they include; data buffering and synchronization due to intermittent connectivity.
Addressing privacy and security concerns
Unauthorized access and attacks on health data pose a severe threat to patient trust and regulatory compliance. To mitigate these risks, it is essential to implement features such as multi-factor authentication, regular security updates, and secure encryption of data both during transmission and while it is stored.
Best Practices for RPM App Development
To address these challenges and develop successful remote patient monitoring applications, developers should adhere to the following best practices
1. Agile development methodologies
Agile practices can be used in developing healthcare projects in such a manner that involves multiple cycles of development, feedback, and changes. This approach helps the developers to easily adapt to the feedback of users and changing regulations.
2. User-centered design principles
Considering both the patients’ and healthcare providers’ perspectives allows for the application to be as user-friendly as possible while fulfilling the needs of all parties. This entails collecting user data, developing users’ profiles, and doing user testing during the entire development phase.
3. Continuous integration and deployment
CI/CD practices are useful to keep the code base clean and reduce the possibility of errors as well as to speed up the process of changes and enhancements to the RPM system. This approach enables fast delivery of new features and fixing of bugs without compromising system stability.
4. Automated testing and quality assurance
The application tests include automated tests, which assist in finding problems and their eventual solution before the actual deployment of the program. This should encompass unit tests, integration tests, as well as, end-to-end tests which are tests performed under the likely usage of the product.
5. Maintenance and support:
Support is vital to ensure that any problems are fixed and the RPM system is current in terms of security patches and feature updates. This includes the creation of a technical support staff, having a reliable issue reporting and tracking procedure, and making periodic software revisions.
Future of RPM Technology
Looking at the enhancement of technology, the future of remote patient monitoring seems to be bright. Several emerging trends are shaping the landscape of RPM: Several emerging trends are shaping the landscape of RPM:

1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
These technologies allow for the collection of extensive patient data and enable pattern analysis, which supports predictive decision-making for patient care. Additionally, AI chatbots can assist with patient identification and provide basic health advice, thereby reducing the burden on healthcare facilities.
2. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
Internet of medical things for the monitoring of a patient’s health status through a network of connected medical devices and wearable gadgets. These sophisticated sensors can monitor various health-related aspects and even detect impending ailments.
3. 5G connectivity
The new 5G networks shall improve data transmission to allow frequent monitoring and also facilitate more telemedicine services. This will be of great help, especially in the rural regions where health facilities are hard to come by.
4. mHealth
M-health applications will remain important tools that can help patients take charge of their health and enhance their interaction with healthcare providers. These apps will evolve to provide better health advice and to be fully compatible with other health services.
5. Patient Compliance
As more enhanced RPM systems are developed, they will integrate some of the components that can enhance patient compliance with their treatment and drug regimens. This might include gamification elements, reminding and encouraging the use of healthy behaviors through AI coaching.
There are numerous opportunities for innovation concerning the development of RPM apps. This can allow developers to concentrate on building more individualistic solutions, use, and open AI benefits, and enhance RPM compatibility with other healthcare technologies like telehealth systems. It is also possible to introduce more unique RPM solutions for certain diseases or groups of patients.
However, as the systems of remote patient monitoring are gaining more popularity, the issues of scaling such solutions emerge. This includes ensuring that the infrastructure can handle increasing data loads as the number of users grows. Additionally, it involves addressing data security and privacy concerns at a large scale, as well as navigating the challenges of healthcare settings and varying regulatory requirements across different countries.
As for the area of further development, it is possible to consider the combination of RPM with VR and AR technologies. These could be used for creating patient education, or for helping the healthcare providers to visualize the patient information better.
Another great potentiality is the application of blockchain technology to the RPM systems. Blockchain might offer an efficient and secure system for managing patient data and could help to overcome some of the interoperability and data security issues of the existing systems in healthcare.
Conclusion
The adoption of remote patient monitoring software development is accelerating, with more providers leveraging technology to enhance patient care. Whether you are a healthcare provider or a developer, understanding the intricacies of remote patient monitoring applications can help you stay ahead in this rapidly evolving industry.
Looking to develop a custom remote patient monitoring app? Contact our team for expert software solutions tailored to your needs.
FAQs:-
1. How does remote patient monitoring work?
RPM utilizes connected devices to collect health data, which is transmitted securely to healthcare providers for analysis and intervention.
2. What are the benefits of remote patient monitoring?
Benefits include improved patient outcomes, reduced hospital visits, cost savings, and early detection of health issues.
3. Is remote patient monitoring covered by insurance?
Many insurance providers and Medicare offer coverage for RPM services, depending on the specific healthcare plan.
4. What features should a remote patient monitoring app have?
Key features include real-time data tracking, AI-driven alerts, secure cloud storage, and seamless telemedicine integration.
5. What are the challenges in developing RPM applications?
Challenges include ensuring regulatory compliance, maintaining data security, integrating with existing healthcare systems, and achieving user adoption.
Keyur Patel
Co-Founder
Keyur Patel is the director at IT Path Solutions, where he helps businesses develop scalable applications. With his extensive experience and visionary approach, he leads the team to create futuristic solutions. Keyur Patel has exceptional leadership skills and technical expertise in Node.js, .Net, React.js, AI/ML, and PHP frameworks. His dedication to driving digital transformation makes him an invaluable asset to the company.
Get in Touch
Search
Blog Categories


