How the Internet of Medical Things(IoMT) Impacts the Healthcare Industry
Keyur Patel
September 12, 2025
13 min
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is quickly transforming the global healthcare sector, filling it with more opportunities for enhancing patients’ experience while also increasing the efficiency of healthcare processes and decisions. With the increased development in IoMT, patients and healthcare providers are already witnessing the magic of smart connected medical devices and intelligent healthcare systems. In this guide, you will learn about IoMT, the main components of IoMT, its effects on the delivery of care, and how IoMT differs from the IoT.
What Is IoMT
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) refers to the interconnected ecosystem of medical devices, software applications, and healthcare systems that collect, analyze, and transmit medical data over the internet. This rapidly growing field combines the principles of the Internet of Things (IoT) with healthcare technology to create a more efficient, personalized, and data-driven approach to medical care.
IoMT encompasses a wide range of devices, from wearable fitness trackers and smart pills to advanced medical imaging equipment and remote patient monitoring systems. These devices collect various types of health data, such as vital signs, medication adherence, and physical activity levels, which can be shared with healthcare providers in real-time.
The primary goal of IoMT is to improve patient outcomes by enabling more timely and accurate diagnoses, facilitating remote care, and enhancing treatment efficacy. It also aims to reduce healthcare costs by streamlining processes, minimizing hospital readmissions, and promoting preventive care.
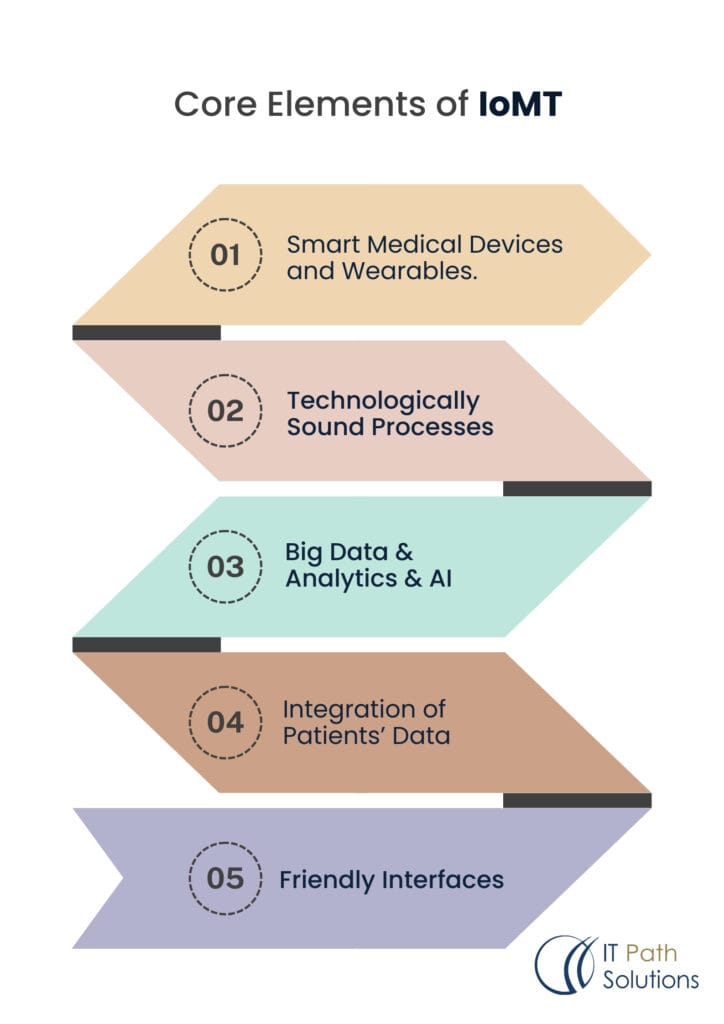
Core Elements of IoMT
The concept and philosophy of IoMT are based on transforming medical devices, sensors, and software applications into an integrated and interoperable entity while providing a holistic and personalized view of the patient’s health data and information. Key components of IoMT include:
- It refers to smart Medical devices and Wearables.
- Technologically sound processes involved in data handling both in transmission and storage media.
- Big data and analytics as well as artificial intelligence.
- Integrated systems that allow for the integration of patients’ data to be transferred easily.
- Friendly interfaces to the healthcare providers and the patient.
It is up to the development companies to make these components of IoMT to be efficient and secure to enhance the quality of patients’ care.
IoMT vs. IoT: A Deeper Dive Into Their Differences
While IoT is a broad concept describing the connection and control of devices in different industries, IoMT is the concept of connecting and controlling medical devices and applications to enhance patients’ quality of life. Based on the requirements of the healthcare industry, IoMT solutions are developed taking into account the stringent regulations, data privacy, and compatibility with the existing medical equipment. The Internet of Medical Things is considered to be an advancement of IoT in healthcare with even enhanced solutions than the IoT.
Impact of IoMT on Healthcare Delivery
The adoption of IoMT is driving significant improvements across various aspects of healthcare delivery:
- Data-Driven Decisions: IoMT platforms allow healthcare providers to obtain the patient’s data in real-time, thus promoting accurate and timely clinical decisions.
- Smart Medical Devices: Smart devices can control the environment, monitor and even alert the staff, as well as offer beneficial data for the patient’s treatment.
- Efficient Processes: IoMT solutions have the potential to improve efficiency, decrease the number of bureaucracy in the healthcare environment, and bring significant changes to the proper usage of resources.
- Global Assistance: Telemedicine and remote monitoring activities enhance the delivery of healthcare to rural areas and increase the reach of the specialist.
- Lower Costs: IoMT therefore results in decreased healthcare costs because it reduces cases of readmission to hospitals, overutilization of resources, and encourages preventive care.
- Improved Patient Experience: They also get improved healthcare and treatment since patients can easily access healthcare information and they get to be more involved in the development of their treatment plans.
- Research and Population Health Management: Due to the increased availability of IoMT devices, a huge quantity of data is collected, which is helpful for medical research and population health programs.
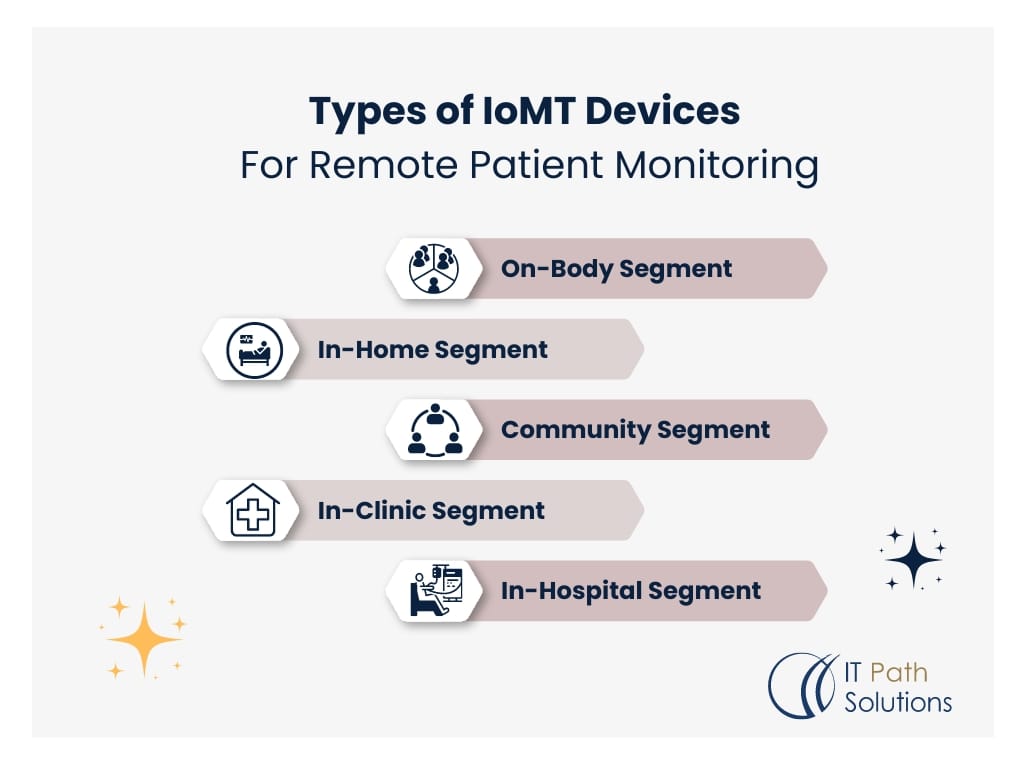
Types of IoMT Devices for Remote Patient Monitoring
IoMT devices can be categorized into several segments based on their use and location: IoMT devices can be categorized into several segments based on their use and location:
- On-Body Segment: Smartwatches, fitness trackers, and ECG monitors that people wear on their hands or wrists.
- In-Home Segment: Integrated weights, sphygmomanometers, and pill boxes.
- Community Segment: The health centers on wheels and telecommunication booths.
- In-Clinic Segment: Diagnostic kits at the patient’s bedside and online health check instruments.
- In-Hospital Segment: Bedside units, syringe pumps, and health facility asset tracking systems.
Mobile application development for IoMT is essential in designing the user interfaces of these devices and the context in which the data generated is understandable to the healthcare providers as well as the patient.
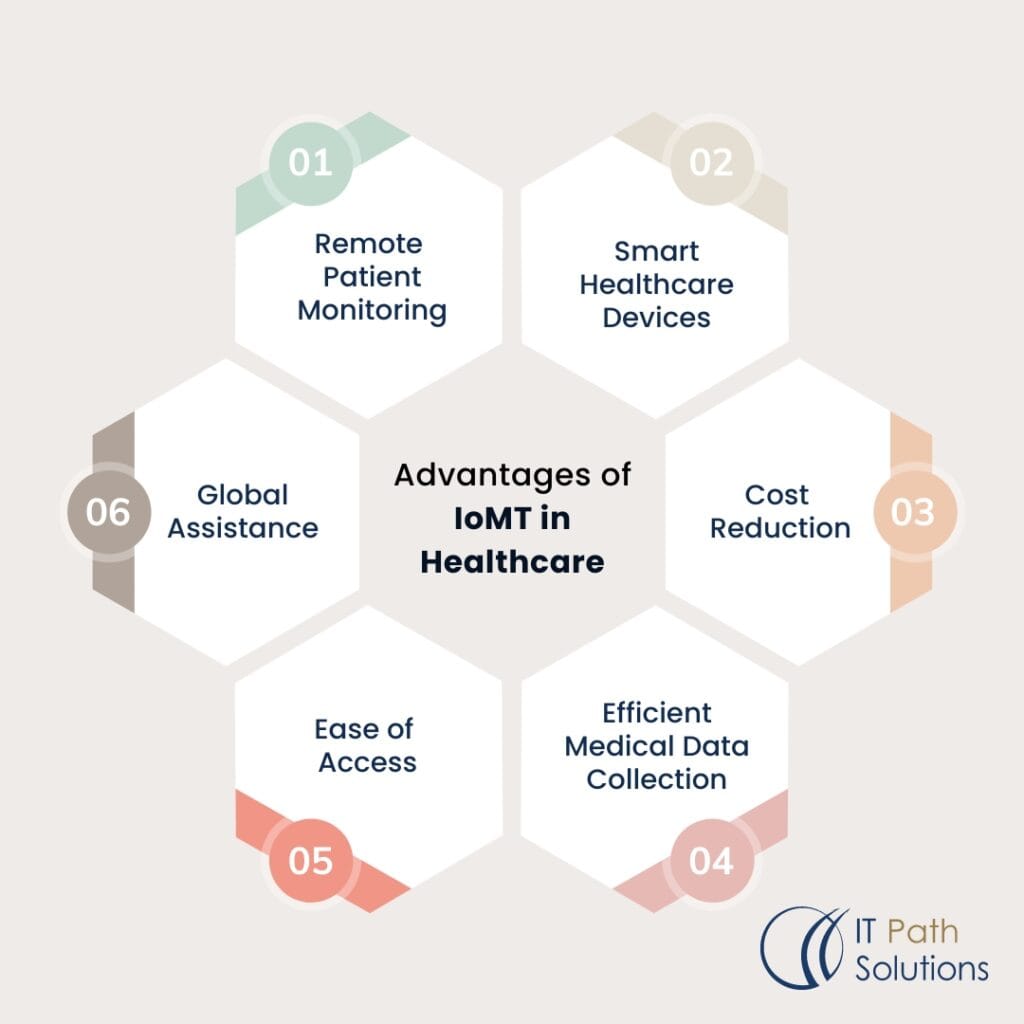
Advantages of IoMT in Healthcare
The adoption of IoMT offers numerous benefits to healthcare providers and patients: The adoption of IoMT offers numerous benefits to healthcare providers and patients:
- Remote Patient Monitoring: This is because the constant monitoring of the health parameters of a patient helps in the early detection of problems and therefore the patient does not need to be readmitted to the hospital frequently.
- Smart Healthcare Devices: Smart healthcare equipment enhances the efficacy of the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
- Cost Reduction: Improved efficiency and shorter hospitalization contribute to the best result in terms of cost.
- Efficient Medical Data Collection: Computer-assisted collection of data eliminates errors and enhances the quality of the records of the patients.
- Ease of Access: Patients can get their health information with ease and also interact with their healthcare providers.
- Global Assistance: Telemedicine services increase health care reach to those who are in rural areas and or those who cannot afford health care.
IoMT Connectivity Technologies and Software Applications
The IoMT ecosystem relies on a variety of connectivity technologies and software applications: The IoMT ecosystem relies on a variety of connectivity technologies and software applications:
- Medical Devices and Equipment: IoMT is built on three components, namely smart sensors, wearable technology, and connected medical devices.
- IoMT Connectivity Technologies: Wireless communication standards such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Cellular Networks, and RFID facilitate wireless data transfer.
- Software Applications: Electronic Health Records (EHRs), patient portals, and analytical workbenches are the systems that handle and analyze IoMT data.
The process of developing an IoMT platform is crucial in building the right system that can enable the healthcare environment to address the data complexities and the integration challenges as they are.
Importance of IoMT in Healthcare Settings
IoMT solutions are making a significant impact across various healthcare environments:
- In-Hospital IoMT: Smart beds, asset tracking systems, and connected medical equipment enhance the functionality of the hospital and the quality of the patients.
- In-home IoMT: Telemonitoring devices and telemedicine technologies allow the patient to have a medical checkup at home.
- On-body IoMT: Wearable technology helps in monitoring health status and has the added advantage of offering individual information.
- Community IoMT: Mobile health clinics and telemedicine kiosks are the solutions that take healthcare facilities to the areas that have no easy access to them.
IoMT is revolutionizing these healthcare settings by enhancing real-time data availability, effective communication between healthcare providers and patients, and enhancing patient care outcomes.
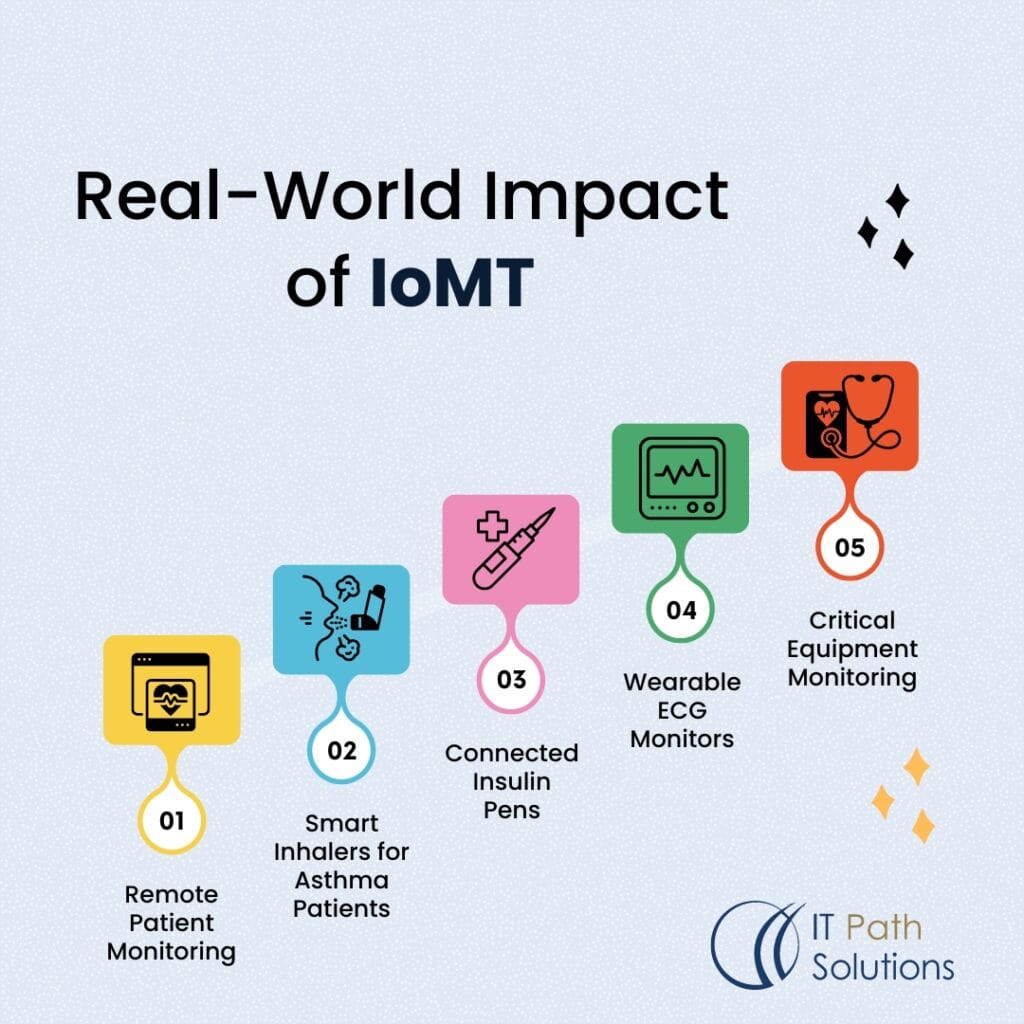
Real-World Impact of IoMT
Several IoMT applications are already transforming healthcare delivery:
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Supervisory care of the key variables and vital signs in patients diagnosed with chronic diseases.
- Smart Inhalers for Asthma Patients: Inhalers for chronic patients that can measure the usage of prescribed medication and, therefore, suggest the best course of action.
- Connected Insulin Pens: New techniques that will enable diabetics to cope with the disease with the help of new insulin delivery gadgets.
- Wearable ECG Monitors: Smart accessories that help in the consistent monitoring of the condition of the heart and identification of heart-related ailments.
- Critical Equipment Monitoring: IoMT solutions, which are associated with tracking the location and status of important instruments deployed in healthcare centers.
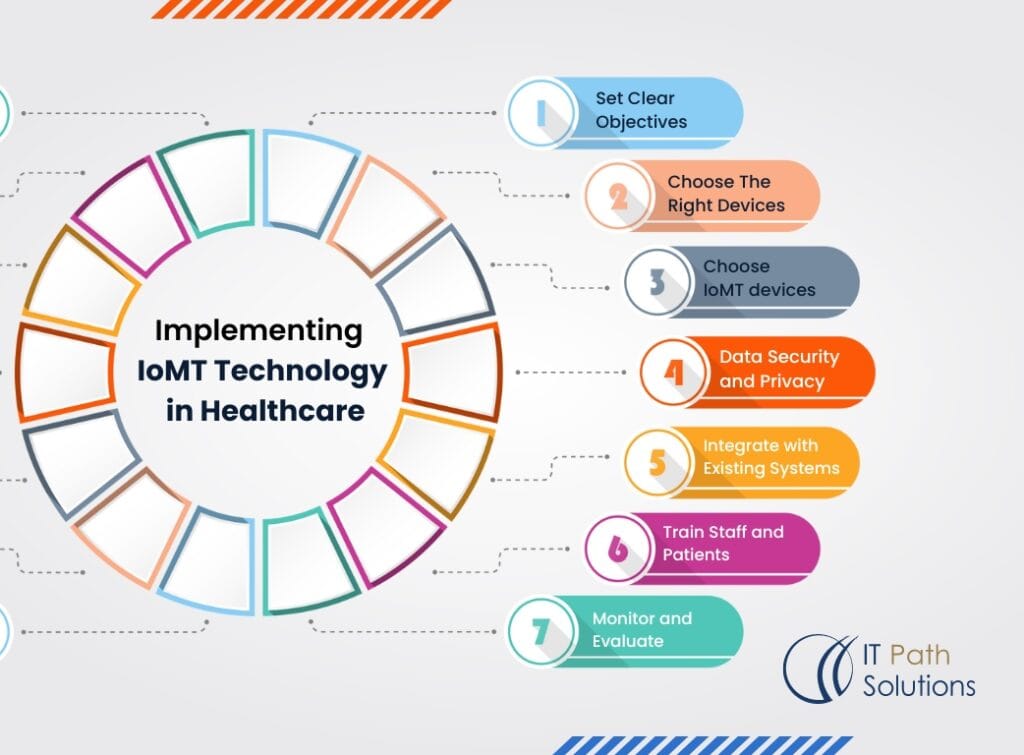
Implementing IoMT Technology in Healthcare
To successfully implement IoMT solutions, healthcare organizations should follow these key steps:
- Set Clear Objectives: Clear use cases and expected outcomes must be determined when IoMT is set in place.
- Choose the Right Devices: Choose appropriate IoMT devices and solutions for an organization’s needs and goals.
- Ensure Data Security and Privacy: Ensure that patients ‘identifying information is safeguarded so as not to compromise their privacy.
- Integrate with Existing Systems: This increases the compatibility of IoMT solutions to interconnect with the current healthcare IT framework.
- Train Staff and Patients: For proper utilization of IoMT technologies, there should be adequate training given to the users and the specialists.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Monitor the improvement brought by IoMT solutions and modify as needed.
Thus, engaging with mature IoMT players can facilitate the correct approach to these steps and proper IoMT technology adoption in healthcare organizations.
Challenges and Solutions for IoMT Implementation
While IoMT offers numerous benefits, healthcare organizations must address several challenges: While IoMT offers numerous benefits, healthcare organizations must address several challenges:
- Business and Infrastructure Cost: Sustainably control costs through a phasic-timing sequence by which implementation takes place.
- Scalability: Select cloud solutions that can be easily scaled up to accommodate organizational requirements.
- Data Accuracy: Ensure the highest standards of data validation and quality of the intelligent connected medical technologies and devices.
- Interoperability: Implement the use of a common standards interface and emphasize APIs for inter-systems interoperability.
Health IT vendors are in a unique position to manage the problems by developing durable, scalable, and integrative solutions to suit the requirements of different healthcare institutions in the process of IoMT development.
Leading IoMT Companies and Solutions
Several companies are at the forefront of IoMT development:
- GE Healthcare: Offers a wide range of connected medical devices and analytics platforms.
- Philips Healthcare: Provides innovative IoMT solutions for both hospital and home care settings.
- DexCom: Specializes in continuous glucose monitoring systems for diabetic patients.
- Cerner Corporation: Develop integrated IoMT platforms for healthcare providers.
- Boston Scientific: Offers connected medical devices for various therapeutic areas.
These IoMT companies are driving innovation in the field, creating new IoMT solutions that address critical healthcare challenges and improve patient outcomes.
Future of IoMT
The future of IoMT holds immense potential for further transforming healthcare delivery. As IoMT development continues to advance, we can expect to see:
- Increased integration of AI and machine learning in IoMT solutions
- More personalized and predictive healthcare interventions
- Enhanced interoperability and data sharing between different healthcare systems
- Greater emphasis on patient engagement and self-management through IoMT applications
- Continued innovation in wearable and implantable medical devices
IoMT platforms will play an increasingly central role in healthcare delivery, enabling more sophisticated data analysis, real-time decision support, and personalized treatment plans.
Emerging Trends in IoMT Development
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is rapidly evolving, with several key trends shaping its development. IoMT solutions are becoming more sophisticated, incorporating advanced analytics and AI to derive meaningful insights from collected data. There’s a growing focus on interoperability, enabling efficient interaction between different healthcare systems and devices.
UI/UX Designs
User interface design is prioritizing both patient appeal and healthcare provider efficiency. Remote patient monitoring applications are expanding, particularly for chronic disease management. Telehealth apps are proliferating due to the increased demand for remote healthcare services. Wearable medical devices are becoming more advanced, offering comprehensive health monitoring and compatibility with other IoMT gadgets.
HIPAA Compliance
HIPAA compliance remains a critical concern, with developers prioritizing secure data handling. Efforts to enhance IoMT security are intensifying to protect sensitive medical information. Interoperability solutions are focusing on creating specific connection interfaces and improving interactions between IoMT and existing healthcare systems.
Advanced Integrations
Advanced healthcare data integration platforms are emerging to centralize and analyze data from various IoMT devices. AI and machine learning are being leveraged to enable more precise diagnoses and personalized treatments. There’s also a trend towards developing more effective models for analyzing the vast amounts of data collected by IoMT devices.
FDA Certification
FDA certification is becoming increasingly important for IoMT solutions, ensuring safety and efficacy. Patient engagement is a key focus, with solutions designed to improve self-management. Cloud-based IoMT applications are gaining traction, offering flexibility and easy deployment. Overall, IoMT product engineering is moving towards full-service solutions, addressing development from ideation through integration and support.
Conclusion
IoMT has the potential to transform healthcare by introducing elements of individualization, optimization, and informationalization in the delivery of medical services. We can foresee a new approach to the expansion of IoMT companies’ influence and the adoption of such revolutionary technologies by healthcare providers that will make IoMT platforms the key to further enhancement of patient health and healthcare services quality. The further evolution of IoMT’s development along with an expanding environment of IoMT solutions promises to revolutionize the healthcare industry in the years to come allowing for previously unimaginable levels of patient care, organizational effectiveness, and data-driven decision-making.
FAQs:-
How does IoMT improve remote patient monitoring?
IoMT uses wearable sensors and connected devices to collect real-time patient health data, allowing doctors to monitor patients remotely. This enables early detection of health issues, reduces the need for frequent in-person visits, and improves management of chronic conditions.
What are the security risks of IoMT in healthcare?
IoMT devices and systems can be vulnerable to cyberattacks, leading to data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive patient information. Risks include data tampering, privacy violations, and device malfunction. Robust encryption, secure authentication, and regular security updates are crucial to mitigate these risks.
How does IoMT reduce healthcare costs?
IoMT reduces costs by enabling remote monitoring, which minimizes hospital readmissions and unnecessary clinic visits. It also improves efficiency through better resource management, faster diagnoses, and optimized workflows. Early detection of health problems through IoMT can prevent costly complications.
What are the benefits of IoMT for elderly patients?
IoMT enhances elderly patient care by providing continuous health monitoring, fall detection, medication reminders, and remote communication with caregivers. This promotes independence, improves safety, and allows for timely interventions, leading to better quality of life.
How does IoMT improve hospital efficiency?
IoMT streamlines hospital operations through real-time asset tracking, automated inventory management, improved patient flow, and faster data sharing among healthcare professionals. This results in quicker response times, better resource allocation, and reduced wait times, enhancing overall hospital efficiency.
Keyur Patel
Co-Founder
Keyur Patel is the director at IT Path Solutions, where he helps businesses develop scalable applications. With his extensive experience and visionary approach, he leads the team to create futuristic solutions. Keyur Patel has exceptional leadership skills and technical expertise in Node.js, .Net, React.js, AI/ML, and PHP frameworks. His dedication to driving digital transformation makes him an invaluable asset to the company.
Get in Touch
Search
Blog Categories

